Ethanol and Decarbonization: Driving Clean Growth

Discover how Brazil leads in Ethanol and Decarbonization, driving a global clean energy shift
Ethanol and Decarbonization: Powering a Sustainable Future
As the world grapples with the urgency of climate change, decarbonization has emerged as one of the most pressing global priorities. International commitments such as the Paris Agreement and widespread climate movements have placed a spotlight on practical solutions to reduce emissions. Among these, Ethanol stands out as a proven, scalable, and sustainable path forward. Brazil, recognized as a global leader in biofuels, has long embraced ethanol as a central tool in its decarbonization strategy. With nearly 89% of its cars running on flexible-fuel technology, the nation has successfully embedded ethanol into its transport sector, reducing millions of tons of CO₂ emissions. Ethanol’s versatility extends beyond road transport to aviation, shipping, and even rail, reinforcing its role as a cornerstone of the clean energy transition.
Brazil’s Unique Model for Ethanol and Decarbonization
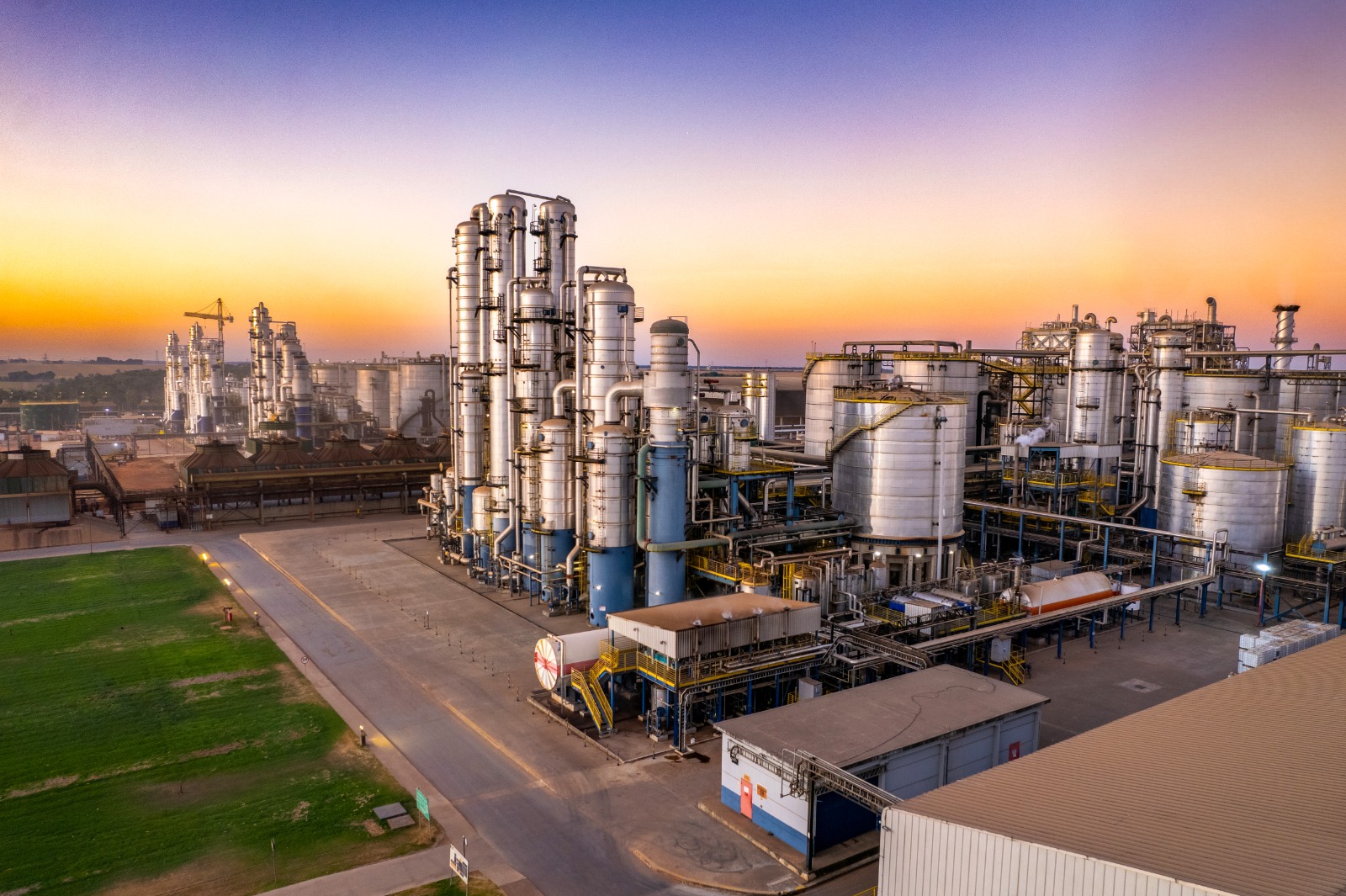
What sets Brazil apart in the conversation about Ethanol and Decarbonization is its agricultural structure. Unlike many regions, Brazil enjoys multiple crops per year. Corn, often grown as a second crop after soybeans, provides abundant raw material without demanding new farmland or threatening food supply. This approach exemplifies how Brazil’s ethanol aligns food security with energy sustainability. Companies such as Inpasa have maximized this advantage.
Inpasa powers its fermentation units with renewable biomass, ensuring energy self-sufficiency and minimal carbon impact. The company also embraces a circular economy model by transforming every part of the corn kernel into ethanol, animal feed, and corn oil. This efficiency ensures that Brazil not only scales production but does so sustainably.
Scaling Ethanol and Decarbonization Globally
Brazil produced 9.73 billion gallons of ethanol in 2024 — enough to power over 25 million flex-fuel cars for an entire year. With expanding refinery capacity, including Inpasa’s fifth plant, the nation is poised to scale even further. Executives stress that ethanol’s scalability makes it uniquely positioned to play a growing role in global decarbonization. Unlike experimental fuels, ethanol is ready now: it is cost-effective, deployable, and supported by decades of proven use. Inpasa, now the largest ethanol producer in Latin America and the second largest globally, exemplifies this growth trajectory. By aligning industrial efficiency with environmental responsibility, the company is leading efforts to make ethanol a competitive solution not just for Brazil, but for international markets.
Looking Ahead: Ethanol and Decarbonization’s Future
The complexity of decarbonization means there is no single solution. Experts highlight the need for a diverse toolkit that includes biofuels, wind, solar, and hydrogen. Still, ethanol remains one of the most effective and immediate tools to accelerate the transition. Brazil’s capacity to expand production without compromising food supply ensures that it will continue to be a key player in the global low-carbon economy. The future of Ethanol and Decarbonization lies in both scaling production and global cooperation. With companies like Inpasa leading the way, Brazil is not only addressing its domestic energy transition but also offering a model for the world. By uniting food security, sustainability and economic development.
Find out more about GSTI Campaign